38 bacterial cell without labels
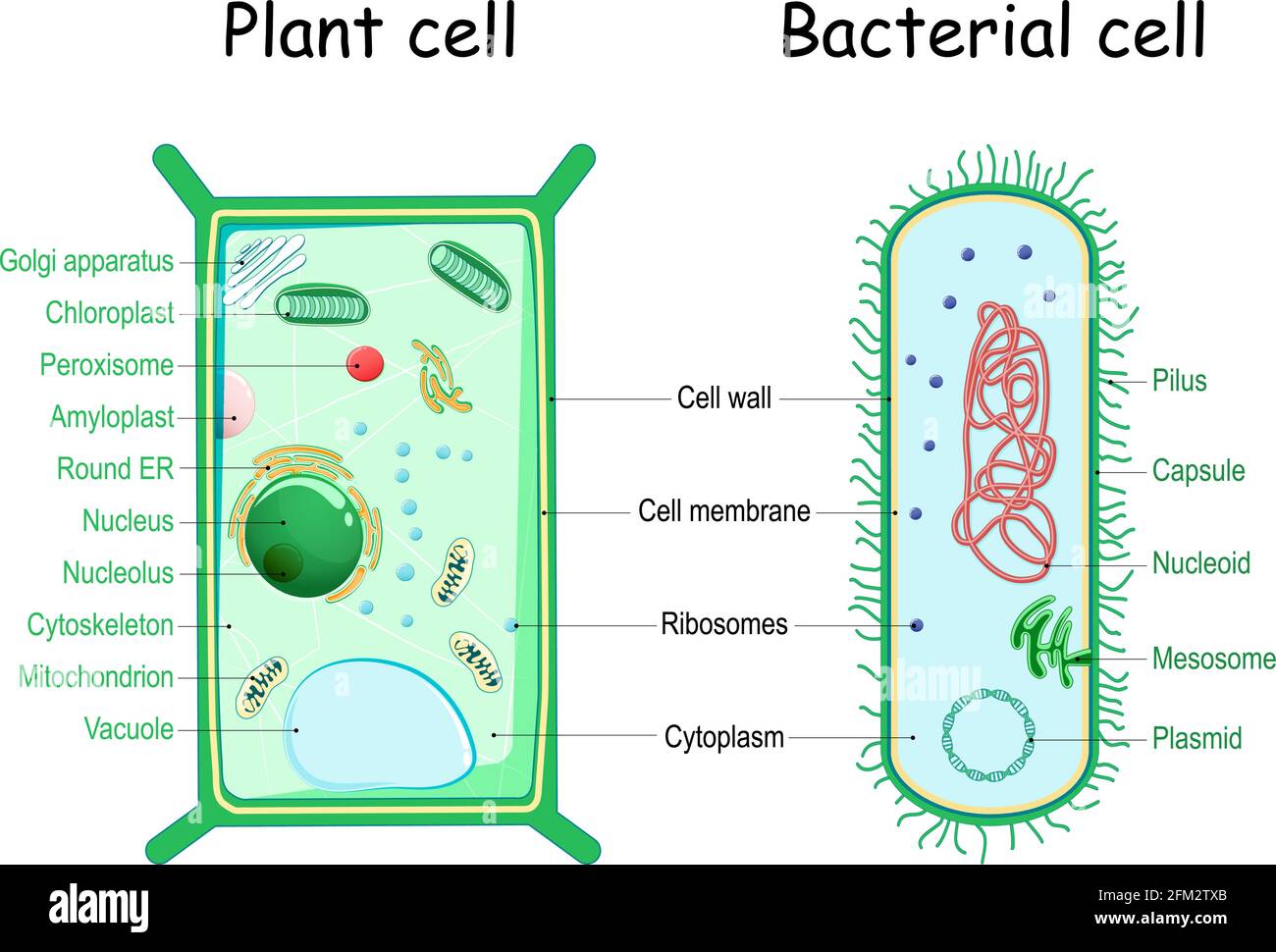
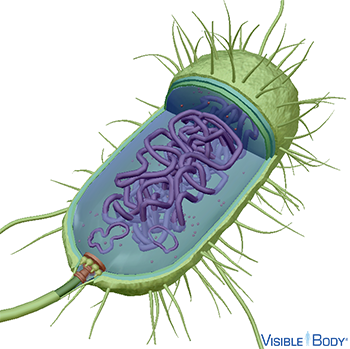
Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram August 14, 2021. Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast. 15 Difference Between Bacterial Cell and Human Cell - Study Read Difference Between Bacterial Cell and Human Cell. The cell is isolated and Independent. It survives as an individual on its own. Human cells are in a group and not isolated. It is dependent on other cells for survival. A thick protective cell wall is present covering the whole cell. Is made of a phospholipid bilayer.
Morphology, Different shapes of bacterial cell - BYJUS These are non-motile, aerobic and gram-positive bacteria that cause many diseases.Examples of streptococci are Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus bovis, Streptococcus agalactiae, etc. Tetrads: Tetrads are arranged in a group of 4 cells.

Bacterial cell without labels
Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification - BYJUS Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles. Vitamins and Supplements Rooted in Science - Life Extension Get clinically-studied, premium vitamins and supplements and lab tests from the people who’ve spent 40 years passionately pursuing healthy living. Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman ... - Nature Raman optical spectroscopy promises label-free bacterial detection, identification, and antibiotic susceptibility testing in a single step. However, achieving clinically relevant speeds and...
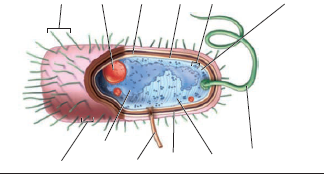
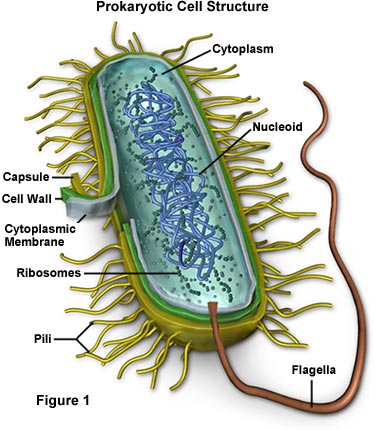
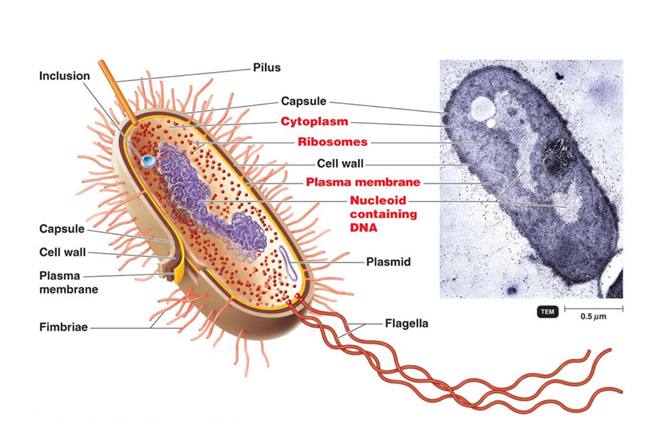
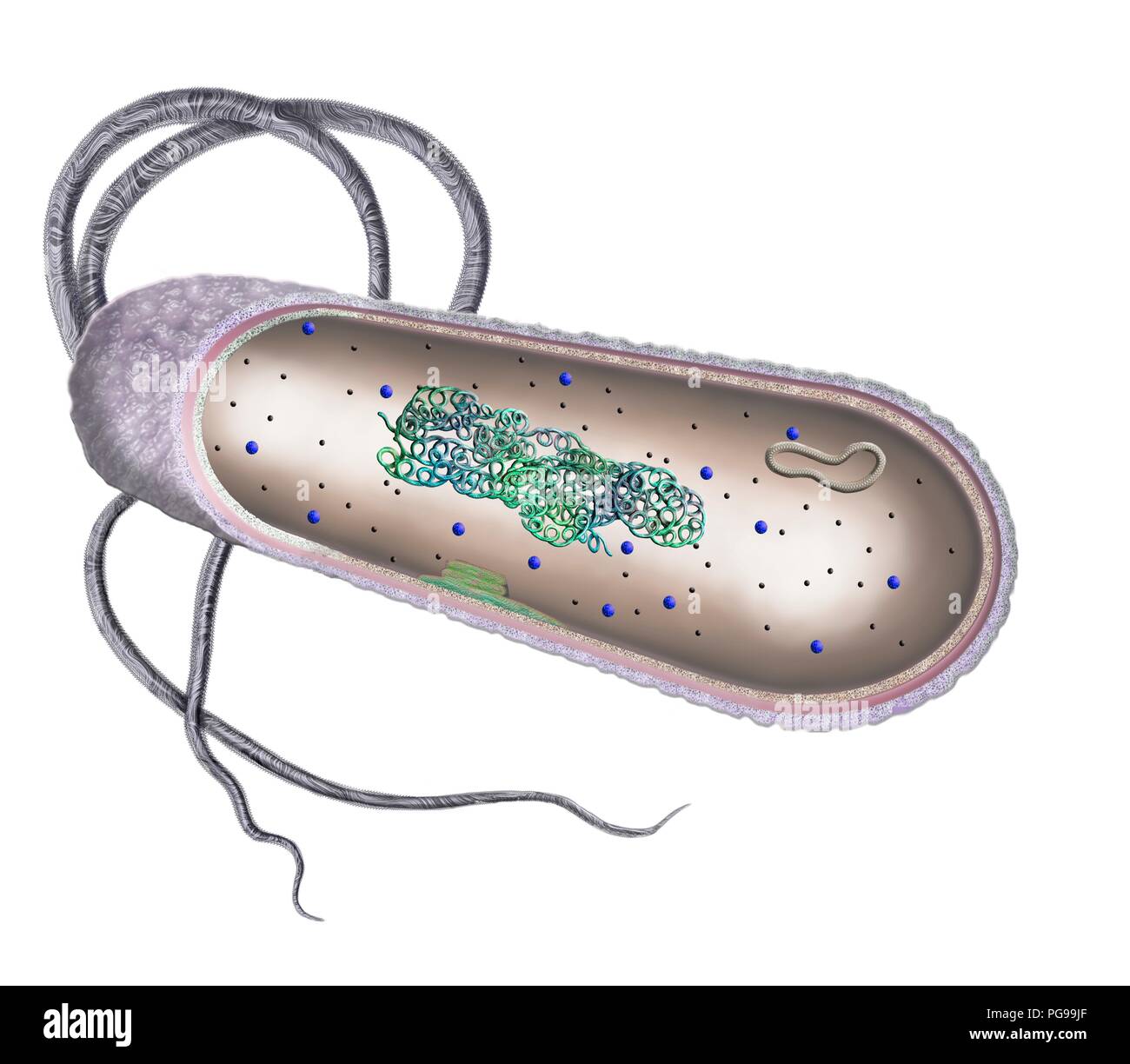
Bacterial cell without labels. Bacterial DNA - the role of plasmids — Science Learning Hub Bacterial DNA - a circular chromosome plus plasmids. The DNA of most bacteria is contained in a single circular molecule, called the bacterial chromosome.The chromosome, along with several proteins and RNA molecules, forms an irregularly shaped structure called the nucleoid. This sits in the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell.. In addition to the chromosome, bacteria often contain plasmids ... 3 Common Bacteria Shapes - ThoughtCo The three basic shapes of bacteria include cocci (blue), bacilli (green), and spirochetes (red). Bacteria are single-celled, prokaryotic organisms that come in different shapes. They are microscopic in size and lack membrane-bound organelles as do eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells and plant cells. Bacteria are able to live and thrive in ... Acronyms and glossary terms | Therapeutic Goods ... Active medical device A medical device that is intended by the manufacturer: to depend for its operation on a source of electrical energy or other source of energy (other than a source of energy generated directly by a human being or gravity); and to act by converting this energy; but does not include a medical device that is intended by the manufacturer to transmit energy, a substance, or any ... Structure - Medical Microbiology - NCBI Bookshelf All bacteria, both pathogenic and saprophytic, are unicellular organisms that reproduce by binary fission. Most bacteria are capable of independent metabolic existence and growth, but species of Chlamydia and Rickettsia are obligately intracellular organisms. Bacterial cells are extremely small and are most conveniently measured in microns (10-6 m). They range in size from large cells such as ...
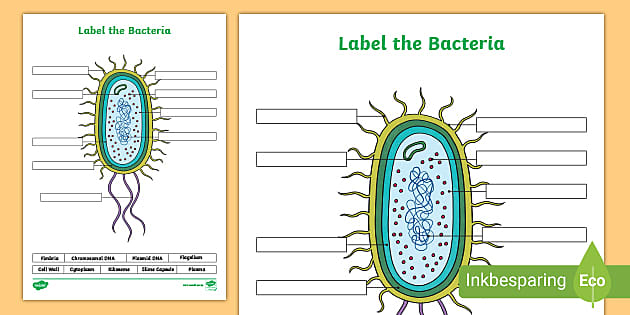
UpToDate {{configCtrl2.info.metaDescription}} Sign up today to receive the latest news and updates from UpToDate. Sign Up Bacterial cells - Cell structure - Edexcel - GCSE Combined Science ... Bacterial cells Bacteria are all single-celled. The cells are all prokaryotic. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes. Larger bacterial... Question : 1) Draw and label a bacterial cell wall with and without a ... Expert Answer. labelling of p …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: (a) Gram-positive bacteria (b) Gram-negative bacteria Carbohydrate portion of lipopolysaccharide wall Cell Peptido- glycan layer Plasma membrane Outer Cell membrane wall Peptido- glycan layer Plasma membrane RRRRR 0000000000 WWW Peptidoglycan traps crystal violet ... Bacterial cells with labels. - Healthclinic Bacterial cells with labels. The spheroid or ovoid or coccus. Bacillus. Vibrio. Spirillum. Spirochaete. Bacterial cells with labels. Bacteria cell anatomy Bacterial cells are microscopic unicellular organisms. The unit of measurement of bacteria is the micrometer (μm) and it is 1/1000 of a millimeter (.001μm).
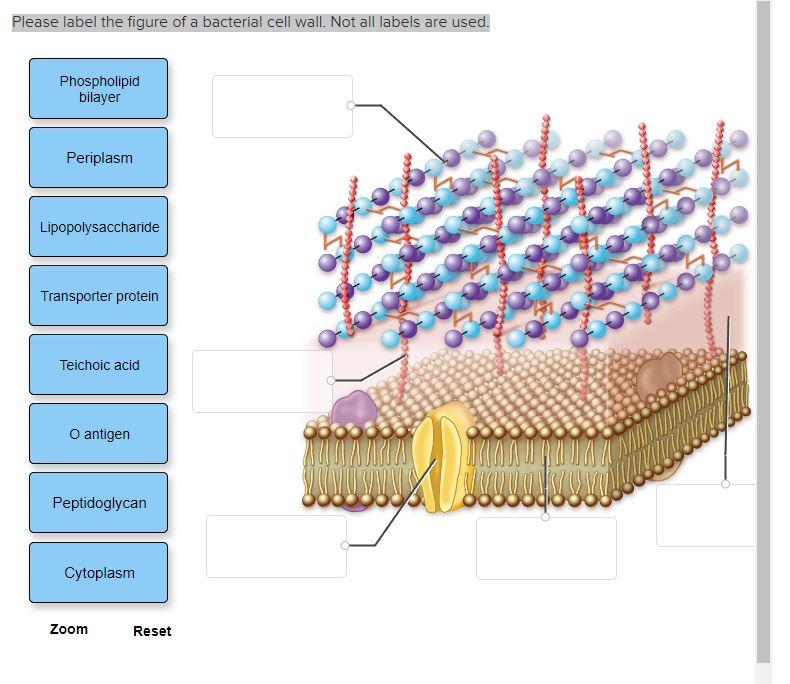
Introduction to Bacteria | Let's Talk Science Bacterial cells are much smaller than human cells. Bacterial cells can measure from about 1 to 10 μm long. Most of them are only about 1 to 2 μm in diameter. 1 μm, or micrometre, is 1 000 times smaller than a millimetre. That is very tiny! It's much smaller than the human red blood cell, which is (on average) about 7 μm in diameter. Bacterial Cell wall: Structure, Composition and Types Cell wall is an important structure of a bacteria. It give shape,rigidity and support to the cell. On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group ie. Gram Positive and gram negative. Types of cell wall 1. Gram positive cell wall Cell wall composition of gram positive bacteria. Peptidoglycan Lipid Teichoic acid Structure of Bacterial Cell (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion It is 10-25 nm in thickness. It gives shape to the cell. Nucleus: The single circular double-stranded chromosome is the bacterial genome. Other structures include cytoplasmic membrane, mesosomes, ribosomes and cytoplasmic inclusions. Unlike eukaryotes cytoplasm does not contain ribosome, Golgi, cytoskeleton. Bacterial Identification| 8 Methods & Tests In Microbiology - Study Read Identification by morphology: This method is to determine the individual bacterial physical appearance. 1. Based on size. Here bacteria are identified based on their physical size. Like small size or big one expressed in microns. For this bacteria are viewed under a microscope to view the size.
Bronchitis - Wikipedia Protracted bacterial bronchitis in children, is defined as a chronic productive cough with a positive bronchoalveolar lavage that resolves with antibiotics. [76] [77] Protracted bacterial bronchitis is usually caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae , non-typable Haemophilus influenzae , or Moraxella catarrhalis . [77]
Bacterial cell structure and function - Online Biology Notes Bacterial are unicellular prokaryotic organism. Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosome, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, peroxisome, glyoxysome, and true vacuole. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus.
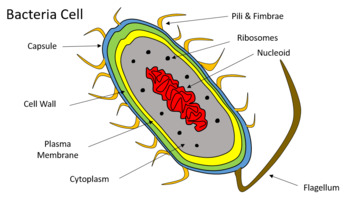
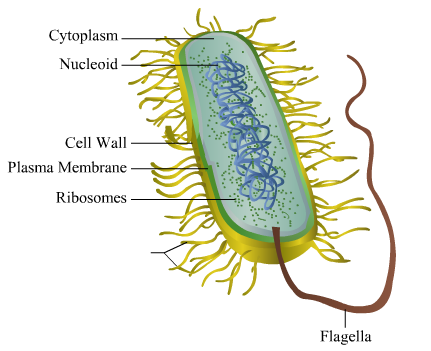
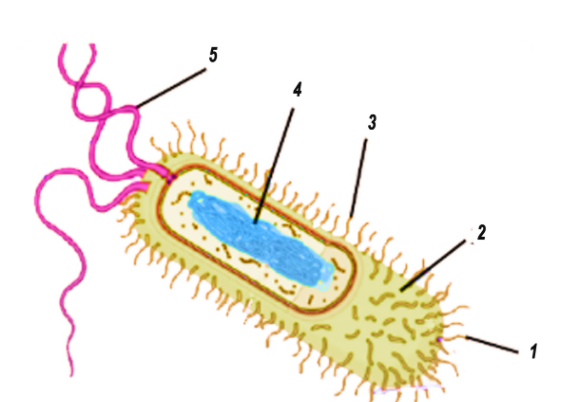
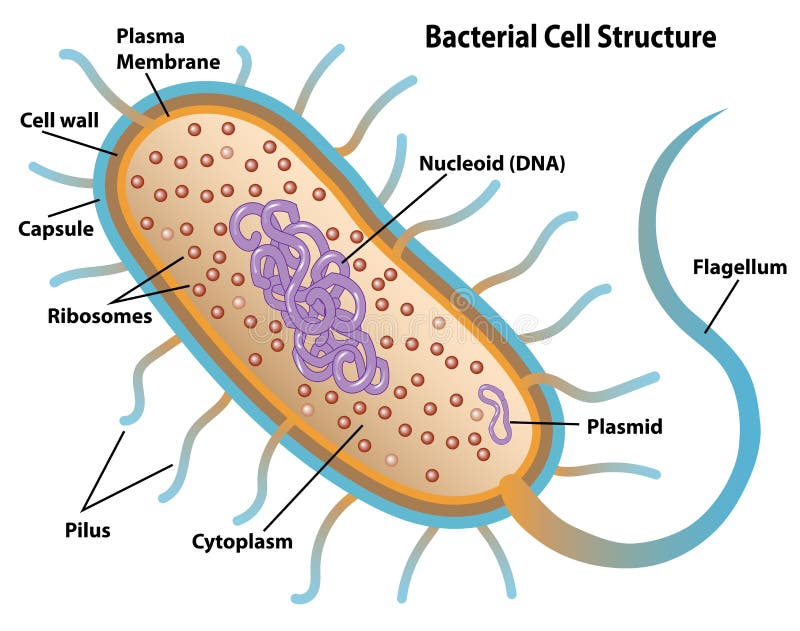
Bacteria Cell: Different Parts of a Generalized Bacteria Cell ... ADVERTISEMENTS: The different parts of a generalized bacteria cell have been-shown in Figure 2.3 and have been described as follows: 1. Flagella: Bacterial flagella are thin filamentous hair-like helical appendages that protrude through the cell wall and are responsible for the motility of bacteria. Most of the motile bacteria possess flagella. Its length is about […]
Bacterial Cell - SlideShare Internal membrane systems: Photosynthetic and cyanobacteria contain internal membrane system (chromometaphore), which has membranes derived from cell membrane (CM) and pigments (helps to capture lights). Nitrifying bacteria, soil organisms those convert nitrogen compounds into forms usable by green plants, also have internal membranes.
Bacteria in Microbiology - shapes, structure and diagram - Jotscroll Bacteria cells are the smallest living cells that are known; even though viruses are smaller than bacteria, viruses are not living cells. In microbiologythere are different types of bacteria with various sizes, shapes, and structures. The bacteria shapes, structure, and labeled diagrams are discussed below. Table of Contents Sizes Bacteria Shapes
Gram-negative bacteria- cell wall, examples, diseases, antibiotics The cell wall of gram-negative bacteria is complex having a thin layer of the peptidoglycan layer of 2-7nm and a thick outer membrane of 7-8nm thick. Microscopically, there is a space that is seen between the cell membrane and the cell wall, known as the periplasmic space made up of periplasm. However it is found in both Gram-negative and Gram ...
Module 2: Bacteria + Archaea Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the images to their corresponding class to test your understanding of bacterial cell shapes 1) coccus - spherical cells 2) bacillus - elongated cylindrical cells - rod-shaped 3) curved variations vibrio spirochete spirillum Gram-positive bacteria have flagella with four basal body rings, while those of gram-negative bacteria have only two
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Bacteria Cell Structure Cytoplasmic Membrane - A layer of phospholipids and proteins, called the cytoplasmic membrane, encloses the interior of the bacterium, regulating the flow of materials in and out of the cell. This is a structural trait bacteria share with all other living cells; a barrier that allows them to selectively interact with their environment.
Bacterial Reproduction and Binary Fission - ThoughtCo Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that reproduce asexually. Bacterial reproduction most commonly occurs by a kind of cell division called binary fission. Binary fission involves the division of a single cell, which results in the formation of two cells that are genetically identical. In order to grasp the process of binary fission, it is ...
Wikipedia:Citation needed - Wikipedia If someone tagged your contributions with a "Citation needed" tag or tags, and you disagree, discuss the matter on the article's talk page.The most constructive thing to do in most cases is probably to supply the reference(s) requested, even if you feel the tags are "overdone" or unnecessary.
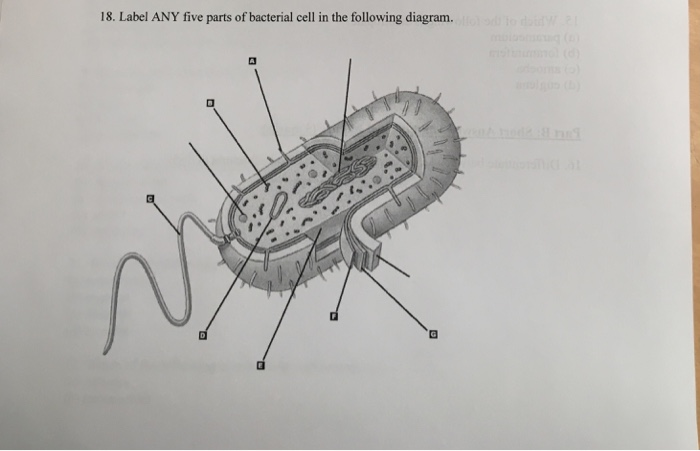
Mapping information-rich genotype-phenotype landscapes ... - Cell Jun 09, 2022 · Mapping the relationship between genetic changes and their phenotypic consequence is critical to understanding gene and cellular function. This mapping is traditionally carried out in one of two ways: a phenotype-centric, “forward genetic” approach that reveals the genetic changes that drive a phenotype of interest or a gene-centric, “reverse genetic” approach that catalogs the diverse ...
Bacterial Cell Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Cytoplasm Water-based solution filling the entire cell Ribosomes Tiny particles composed of protein and RNA that are the sites of protein synthesis Nucleoid Composed of condensed DNA molecules. Cell Membrane A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials in and out of the cell S Layer
The Bacterial Cell Envelope - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Accordingly, E. coli and other enteric bacteria must have a cell envelope that is particularly effective at excluding detergents such as bile salts. This need not be a pressing issue for other Gram-negative bacteria, and their envelopes may differ in species- and environmentally specific ways.
Bacterial Cell: Structure and Components | Microbiology Bacterial cells (prokaryotic cells) are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 3.2. They consists of various cell surface structures, cell wall, plasma membrane, many cytoplasmic inclusions, and the bacterial chromosome (nucleoid). Except some, all structures do not occur in every genus.
Shop by Category | eBay Shop by department, purchase cars, fashion apparel, collectibles, sporting goods, cameras, baby items, and everything else on eBay, the world's online marketplace
Interactive Bacteria Cell Model - CELLS alive Mycoplasma are bacteria that have no cell wall and therefore have no definite shape. Outer Membrane: This lipid bilayer is found in Gram negative bacteria and is the location of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in these bacteria. Gram positive bacteria lack this layer. LPS can be toxic to a host and can stimulate the host's immune system.
Bacteria Label Worksheet Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Need a fun and creative way to introduce bacteria cell structures to your students? This is it! As a color and label activity, students will be able to get creative and productively learn about the structures of the cell!This can easily be modified to increase or decrease difficulty.
Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman ... - Nature Raman optical spectroscopy promises label-free bacterial detection, identification, and antibiotic susceptibility testing in a single step. However, achieving clinically relevant speeds and...
Vitamins and Supplements Rooted in Science - Life Extension Get clinically-studied, premium vitamins and supplements and lab tests from the people who’ve spent 40 years passionately pursuing healthy living.
Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification - BYJUS Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles.















Post a Comment for "38 bacterial cell without labels"